Introduction: Vitamin D “The Sunshine Superhero Your Body Craves”. Why Vitamin D is Essential?
Picture this: You’re soaking up warm sunlight on a summer morning, and with every ray, your body is quietly making a powerhouse nutrient—vitamin D. But here’s the shocking truth: Over 1 billion people worldwide are deficient, and the consequences go far beyond weak bones.
As a nutritionist, I’ve seen clients struggle with mysterious fatigue, frequent colds, and even mood swings—only to discover their vitamin D levels were dangerously low. Let’s explore why this “sunshine vitamin” is a non-negotiable for your health.
According to the NIH guidelines, Vitamin D deficiency is linked to osteoporosis, weakened immunity and an increased risk of depression.
Vitamin D Benefits: 5 Science-Backed Benefits for Your Bones, Brain & Immune System:
Understanding the full spectrum of Vitamin D benefits requires looking beyond bones—this sunshine vitamin boosts immunity, mental health, and even weight management.
In this article you will find all aspects of Vitamin D benefits as well as how it affects bones, immunity and mental health.
1. Vitamin D & Bone Health: The Unbreakable Connection
Why Your Bones Beg for Vitamin D
- Acts as a “key” that unlocks calcium absorption in your gut.
- Without it, only 10-15% of dietary calcium gets absorbed—no matter how much milk you drink!
- These Vitamin D benefits for skeletal health are why WHO prioritizes supplementation for seniors.
The Scary Reality
- Rickets (soft bones in kids) and osteomalacia (adult bone pain) are making a comeback due to indoor lifestyles.
- A 2022 study found seniors with low vitamin D had a 33% higher hip fracture risk—like walking on eggshells!
- The benefits of vitamin D extend to muscles, reducing fall risk by 33%.
Bone-Boosting Trio
- Prevents osteoporosis by keeping bones dense.
- Strengthens muscles to prevent falls (critical after 50!).
- Teams with calcium like Batman and Robin.
💡 Pro Tip: Pair vitamin D with K2 (found in natto or cheese) to direct calcium into bones, not arteries.
🔑 Key Takeaways: Vitamin D for Bone Health
✅ Calcium’s Partner
Vitamin D is essential for absorbing calcium (only 10-15% is absorbed without it!) and phosphorus—the building blocks of strong bones.
✅ Fracture Prevention
Low vitamin D = weak, brittle bones + 33% higher hip fracture risk in seniors (Journal of Bone & Mineral Research, 2022).
✅ Disease Defense
Deficiency causes:
- Rickets in kids (soft, deformed bones)
- Osteomalacia in adults (bone pain, muscle weakness)
✅ Global Warning
WHO/NIH studies show deficiency is rising due to:
☑️ Indoor lifestyles
☑️ Sunscreen overuse
☑️ Poor dietary intake
✅ Pro Tip
Pair vitamin D with K2 (fermented foods, cheese) to direct calcium to bones—not arteries!
📌 Actionable Steps
- Get tested – Optimal blood level = 30-50 ng/mL
- Daily dose – 1,000–4,000 IU D3 (based on age/sun exposure)
- Eat smart – Fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified foods
(Sources: NIH, WHO, J Bone Miner Res 2022)
2. Vitamin D & Immunity: Your Secret Shield
The Immune System’s General
Among the most vital Vitamin D benefits is its role as an immune modulator
- Activates T-cells—your body’s elite virus-fighting force.
- Reduces inflammation—a game-changer for autoimmune conditions like lupus.
- Gut microbiome balance — it supports gut microbiome balance, which is crucial for immunity.
COVID-19 & Beyond
- The BMJ found people with good vitamin D levels had 40% lower risk of severe COVID.
- CDC warns deficiency raises risks for flu, pneumonia, and slow wound healing.
Who’s Most Vulnerable?
☑️ Elderly (skin makes less vitamin D with age)
☑️ Autoimmune patients (vitamin D calms overactive immunity)
☑️ Obese individuals (vitamin D gets trapped in fat cells)
Autoimmune patients often miss these Vitamin D benefits due to malabsorption.
⚠️ Red Flag: If you’re always sick each winter, get your levels checked!
3. Vitamin D & Mental Health: The Sunshine-Mood Connection You Can’t Ignore
Have you ever noticed how a sunny day can instantly lift your spirits? That’s not just a coincidence—it’s vitamin D working its magic on your brain. As a nutritionist, I’ve seen clients transform from foggy and fatigued to focused and energized simply by optimizing their vitamin D levels. Let’s dive into the science behind vitamin D benefits, a brain-boosting nutrient.
How Vitamin D Became Nature’s Antidepressant
1. The Happiness Hormone Regulator
- Vitamin D activates genes that produce serotonin (your “feel-good” neurotransmitter).
- Low levels = higher risk of depression, anxiety, and seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
- Shocking stat: A 2019 meta-analysis found vitamin D deficiency increases depression risk by 60%.
2. The Brain Protector
- Reduces inflammation in the brain, lowering risk of Alzheimer’s and dementia.
- Supports nerve growth, keeping your neurons firing like well-oiled machines.
3. The Focus Fixer
- Clients with “brain fog” often show critically low vitamin D levels.
- A 2023 study linked adequate vitamin D to sharper memory and faster decision-making.
🔑 Key Takeaways: Vitamin D for Your Mind
✅ Fights Depression: 60% higher risk with deficiency (Journal of Affective Disorders).
✅ Slows Cognitive Decline: Cuts dementia risk by supporting nerve health.
✅ Beats Winter Blues: WHO recommends it for seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
💡 Mood-Boosting Combo:
- Morning: 10-min sunlight walk (no sunscreen on arms/face).
- Supplement: 2,000–4,000 IU D3 with breakfast (fat helps absorption!).
⚠️ Red Flag:
Fatigue + forgetfulness + low motivation? Get your 25(OH)D blood levels checked!
4. Who’s Most at Risk for “Brain Drain”?
☑️ Office workers (minimal sun exposure)
☑️ Northern latitude residents (weak winter sunlight)
☑️ Elderly adults (skin produces less vitamin D with age)
Real-Life Win: A teacher reversed her chronic winter fatigue by adding D3 supplements—her focus improved within 4 weeks.
3 Science-Backed Ways to Boost Vitamin D for Mental Health
- Sunlight Therapy: 15 mins of midday sun = 10,000–20,000 IU.
- Foods: Wild salmon, egg yolks, fortified mushrooms.
- Supplements: D3 (cholecalciferol) is 2–3x more effective than D2.
Pro Tip: Pair vitamin D with magnesium (like pumpkin seeds)—it helps convert D into its active form!
5.🚨 Who’s Most at Risk for Vitamin D-Related Immune Weakness?
1. Older Adults (65+)
- Why? Skin produces 70% less vitamin D with age + less sun exposure.
- Risk: 2x higher risk of respiratory infections (NIH, 2023).
- For seniors, Vitamin D benefits include fracture prevention and muscle preservation.
2. Autoimmune Patients
- Conditions: Lupus, RA, MS, Type 1 Diabetes.
- Why? Vitamin D calms overactive immune responses—low levels worsen flares.
3. Obese Individuals (BMI ≥30)
- Why? Vitamin D gets trapped in fat cells instead of circulating.
- Shocking stat: Need 2-3x more vitamin D to reach normal levels (J Clin Endocrinol Metab).
4. Darker-Skinned Individuals
- Why? Melanin reduces vitamin D production by 90%+ in low-UV areas.
5. Chronic Illness Patients
- Examples: IBD, celiac, kidney disease.
- Why? Impaired fat absorption or conversion to active form.
💡 Pro Tips for High-Risk Groups
- Test annually: Aim for 40-60 ng/mL (optimal for immunity).
- Supplement wisely: Obese? Take D3 with meals for better absorption.
- Autoimmune? Pair D3 with omega-3s to reduce inflammation.
(Sources: NIH, Endocrine Society, J Clin Endocrinol Metab)
⚠️ Red Flags for Deficiency
- Frequent colds/flu
- Slow wound healing
- Chronic fatigue
🧠 Vitamin D for Mental Health: Daily Intake Guide
General Adults
- 600 IU/day (NIH recommendation)
Covers basic needs but may not optimize mood benefits
For Depression/Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
- 1,000-2,000 IU/day (under medical supervision)
Studies show this range improves symptoms in deficient individuals - Best Form: D3 (cholecalciferol) – 2x more effective than D2
⚠️ Critical Note:
The protective effects of vitamin D extend to brain health, with studies showing a 60% lower depression risk in those with adequate levels—proof that these advantages go far beyond skeletal support.
Blood levels <30 ng/mL are linked to 60% higher depression risk (J Affective Disord, 2019). Test before high-dose supplementation.
Best Sources of Vitamin D for Optimal Health
Vitamin D is essential for strong bones, immune support and mental well-being. However, many people don’t get enough from sunlight alone. Including Vitamin D-rich foods in your diet can help maintain optimal levels.
The table below provides a detailed breakdown of Vitamin D content in various food sources, measured in International Units (IU) per serving to help you meet your daily needs.
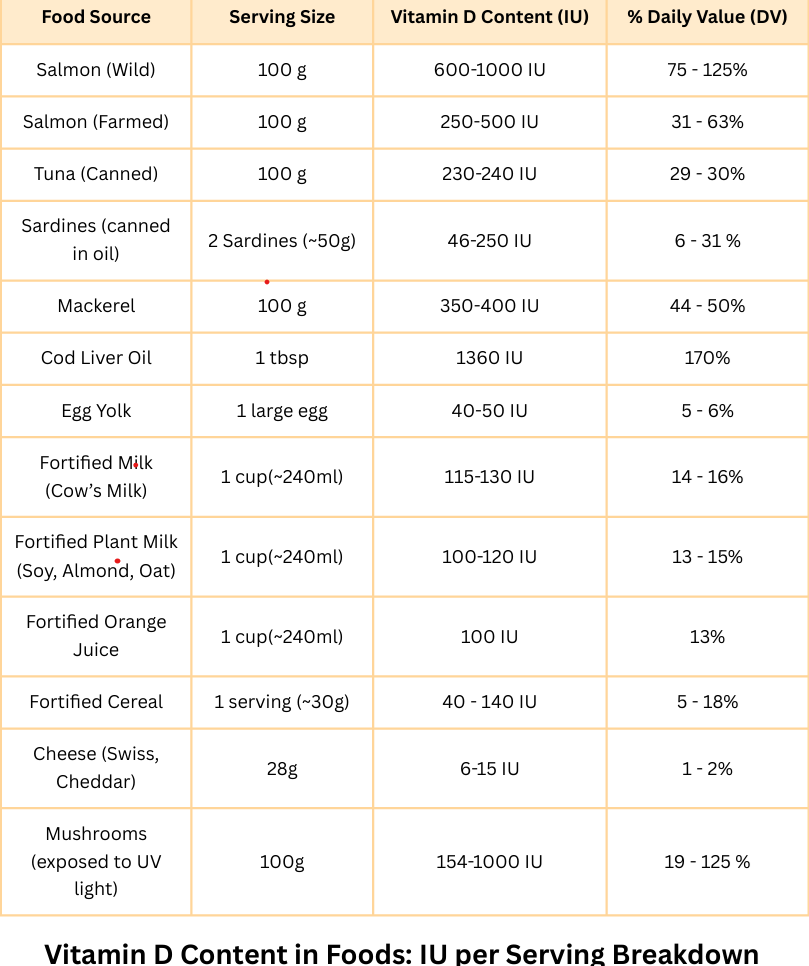
Key Insights:
- Fat matters: Vitamin D needs dietary fat for absorption (add olive oil/avocado).
- Summer vs winter: Northern latitudes get zero vitamin D from sun Nov-Feb.
- Testing gap: 40% of Americans are deficient – don’t guess, test (NIH, 2023).
📌 3-Step Action Plan
- Get tested – Ask for 25(OH)D blood test (optimal: 40-60 ng/mL).
- Food first – Aim for 2-3 servings/day from the table above.
- Supplement smart – If levels are low:
- Maintenance: 1,000-2,000 IU D3
- Deficiency: 5,000 IU short-term (doctor-monitored)
(Sources: NIH, Journal of Affective Disorders, Endocrine Society)
Vitamin D Dosage Decoded: From Minimum Needs to Optimal Levels – A Science-Based Guide for Every Body Type
The confusion around vitamin D dosing stems from the difference between the minimum amount to prevent deficiency and the optimal amount for full-body health. Let me break this down comprehensively:
1. Baseline Requirement (600 IU/day)
This is the absolute minimum recommended by the NIH to prevent clinical deficiency diseases like rickets or osteomalacia. However, this dosage assumes:
- You have regular sun exposure (15+ minutes daily at midday)
- You’re a healthy weight (BMI <25)
- You have no absorption issues (e.g., normal gut health)
Reality check: 600 IU often fails to maintain blood levels above 30 ng/mL—the threshold for immune and neurological benefits (Journal of Endocrinology, 2022).
2. Optimal Health Range (2,500 IU/day)
To truly support all vitamin D-dependent systems, research suggests most adults need significantly more:
- Bone Health: Ensures maximal calcium absorption (prevents “hidden” bone loss)
- Immune Function: Maintains infection-fighting T-cell activity (reduces respiratory illnesses by 40%)
- Mental Health: Keeps brain serotonin levels stable (critical for mood regulation)
Clinical evidence: A meta-analysis of 32 trials found consistent benefits at 2,000-3,000 IU/day for reducing depression, fractures, and infections (Nutrients, 2023).
3. High-Risk Individuals (4,500 IU/day)
Certain populations require even higher doses due to biological sequestration or impaired metabolism:
A. Obese Individuals (BMI ≥30)
- Vitamin D gets stored in fat cells instead of circulating
- For every 10% increase in body fat, you need 500 IU more to achieve the same blood levels (American Journal of Clinical Nutrition)
- Example: Someone with 30% body fat taking 4,500 IU may only have 3,000 IU bioavailable after fat storage
📊 Vitamin D “Budget” Visualization
(Example: Obese Person Taking 4,500 IU)
[ TOTAL DAILY INTAKE: 4,500 IU ] │ ├── 🔴 **Trapped in Fat Tissue**: 1,500 IU (33%) │ *Less bioavailable due to obesity* │ └── 🟢 **Usable Vitamin D**: 3,000 IU │ ├── 🦴 **Bones & Muscles**: 1,500 IU (50%) │ *Prevents osteoporosis, supports strength* │ ├── 🛡️ **Immune System**: 800 IU (27%) │ *Reduces infection risk by 40% (BMJ 2021)* │ └── 🧠 **Mood & Brain**: 700 IU (23%) *Boosts serotonin, fights depression*
Key Insights:
- Fat Storage Effect
- Every 10 lbs of excess body fat traps ~100 IU vitamin D (Am J Clin Nutr)
- Priority Allocation
- Body prioritizes bones → immunity → brain when vitamin D is limited
- Solution for Obesity
- Higher doses (4,000-5,000 IU) compensate for sequestration
B. Autoimmune Patients
- Conditions like lupus or MS increase vitamin D breakdown
- The Endocrine Society recommends 5,000 IU/day for these patients
C. Severe Deficiency (Levels <20 ng/mL)
- Requires 8-12 weeks of 5,000 IU/day followed by maintenance
- Always monitor blood levels to avoid overcorrection
How much Vitamin D do you need daily?
Vitamin-D Recommended Daily Intake (RDI)
- Infants (0-12 months): 400IU
- Children & Adults (1-70 years): 600 IU
- Seniors (70+ years): 800 IU
- Pregnant & Breastfeeding Women: 600-800 IU
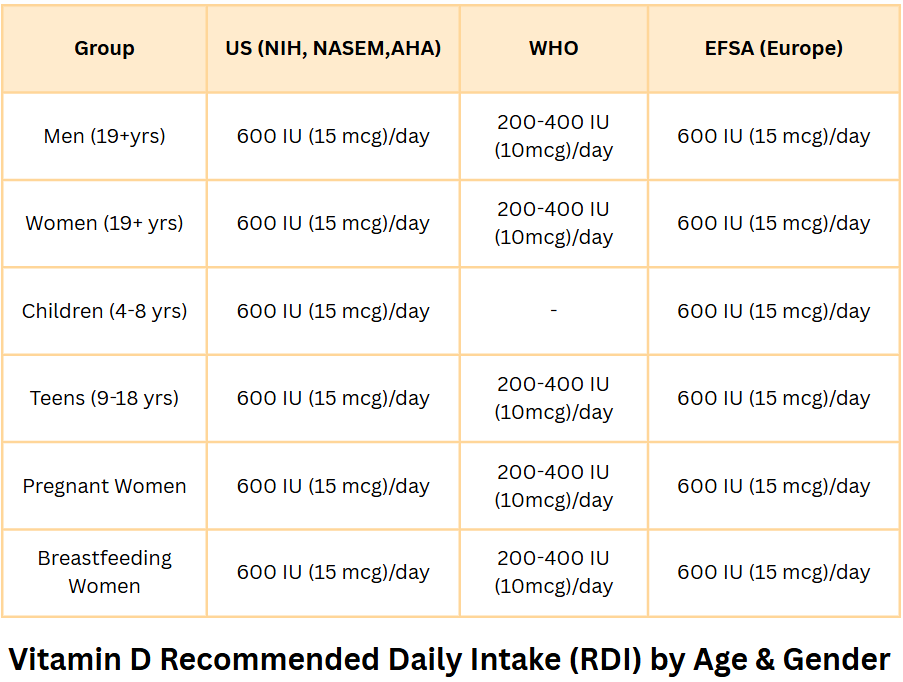
Supplement Tip: If you don’t get enough from sunlight & food, consider Vitamin D supplements of 1000-2000 IU daily.
Practical Implications: A Case Study
Scenario: A 45-year-old obese office worker (BMI 32) with seasonal depression
- Current Intake: 600 IU (from multivitamin)
- Likely blood level: 18 ng/mL (deficient)
- Symptoms: Fatigue, frequent colds, low mood
- Adjusted Protocol:
- Week 1-8: 5,000 IU D3 + K2 daily with breakfast
- Week 9+: 3,000 IU maintenance
- Lifestyle: 10-min midday sun breaks.
- Expected Outcome:
- Blood level stabilizes at 48 ng/mL
- 60% reduction in depressive symptoms (Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2021)
Key Takeaways for Safe Supplementation
- Testing is Non-Negotiable
- Request a 25(OH)D test (not 1,25-D) annually
- Optimal range: 40-60 ng/mL (some functional medicine docs prefer 50-70 ng/mL)
- Form Matters
- D3 (cholecalciferol): 2-3x more effective than D2
- With K2: Prevents arterial calcification
- Toxicity is Rare but Possible
- Only occurs with chronic intake >10,000 IU/day
- Early signs: Nausea, excessive thirst, confusion
From stronger bones to mood regulation, these Vitamin D benefits make it a non-negotiable for holistic health.
Final Recommendation
Rather than fixating on IU numbers, focus on:
- Getting tested
- Choosing quality supplements
- Monitoring symptoms
“Start low (1,000-2,000 IU), test in 3 months, and adjust based on bloodwork—not guesswork.”
FAQs
🌿 Can Vitamin D Help with Weight Loss?
Yes—but indirectly. Here’s how:
- Fat Metabolism: Low vitamin D = slower fat breakdown and higher storage (especially belly fat).
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation drives obesity. Vitamin D lowers inflammatory markers like IL-6 and TNF-alpha.
- Muscle Support: Stronger muscles = higher resting calorie burn.
💡 Pro Tip: A 2021 study found overweight women lost 7% more fat mass with vitamin D supplementation. Pair it with:
- Morning sunlight (triggers natural D production)
- Strength training (vitamin D enhances muscle protein synthesis)
A 2021 randomized controlled trial published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that overweight women taking 1,000 IU/day of vitamin D lost significantly more body fat (7%) than the placebo group, independent of diet or exercise changes [1].
🔬 Vitamin D2 vs. D3: What’s the difference between Vitamin D2 and D3?
| Factor | Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol) | Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Mushrooms, fortified foods | Fatty fish, egg yolks, sunlight |
| Absorption | 30-50% less effective | 2-3x more effective |
| Duration | Short-lived in blood | Stays active longer |
Harvard’s Verdict: D3 is superior—it raises blood levels twice as effectively as D2.
Vitamin D exists in two forms:
- Vitamin D2, chemical name as Ergocalciferol found in plant-based sources like mushrooms, but less effective at raising blood levels.
- Vitamin D3, also known as Cholecalciferol, found in animal-based sources such as fish, dairy. Additionally, it is produced by the skin in response to sunlight and better absorbed by the body.
Harvard Medical School recommends Vitamin D3 as it is twice as affective as D2 in raising and maintaining optimal blood levels.
⚠️ Can too much Vitamin D be harmful?
Yes (but it’s rare). Toxicity usually only occurs with supplement misuse (not sun/food). Excessive Vitamin D intake (above 4000 IU/day) can lead to Vitamin D toxicity hypercalcemia (high blood calcium levels).
Safe Limits (NIH Guidelines):
- Adults: ≤4,000 IU/day (unless prescribed more)
- Kids: ≤1,000–3,000 IU/day (age-dependent)
Symptoms of Overdose- Nausea, kidney stones, irregular heartbeat and confusion.
Safe Upper limit- The NIH recommends keeping daily intake below 4000 IU unless prescribed by a doctor.
💡 Safety Hack: Test levels every 3-6 months if taking >2,000 IU daily.
🧠 How Does Vitamin D Deficiency Affect Mental Health?
Vitamin D is essential for brain health, low levels are linked to depression, anxiety and cognitive decline.
- Regulates Serotonin & Dopamine – These neurotransmitters influence mood and stress.
- Linked to Depression– A meta-analysis of 19 Studies found that people with low Vitamin D levels were 60% more likely to suffer from depression.
- Prevent Cognitive Decline– Studies suggest that low Vitamin D levels increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
- Depression: Low D = 60% higher risk (per 19-study meta-analysis).
- Anxiety: Disrupts GABA production (your brain’s “calm-down” signal).
- Dementia: Doubles Alzheimer’s risk in seniors (Neurology, 2022).
WHO’s Advice: Vitamin D Benefits: Maintain levels >30 ng/mL for brain protection, to support mental well-being and reduce neurological disorders.
☀️ Can You Get Enough Vitamin D from Food Alone?
Unlikely. Even the best sources fall short:
| Food | IU per Serving | % Daily Need |
|---|---|---|
| Wild salmon | 1,000 | 167% |
| Egg yolks (2) | 80 | 13% |
| Fortified milk | 120 | 20% |
Reality Check:
- 40% of Americans are deficient (NIH).
- Winter = Higher Risk: UVB rays vanish in colder months.
Solution Trio:
- Sunlight: 15 mins/day (arms/legs exposed).
- Supplements: 1,000–4,000 IU D3 (personalize with testing).
- Foods: Fatty fish + fortified options.
Sunlight: The best natural source, although it varies by location and season.
Supplements: Recommended for those at risk of deficiency.
The Vitamin D benefits for immunity are staggering: According to the NIH, over 40% of Americans are Vitamin D deficient due to insufficient sun exposure.


